- Home Page
- Company Profile
- Our Products
- Contact Us
Showroom
We are one of the leading names that provide robust and efficient Burner Controller devices that are available in various sizes and power ratings. Get these premium-quality controller units with the assurance of fast and safe delivery at a low price.
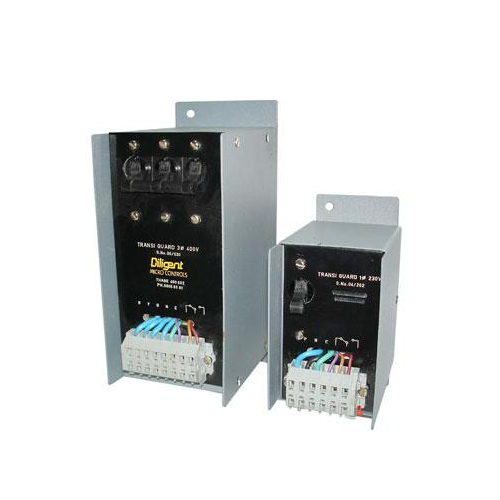
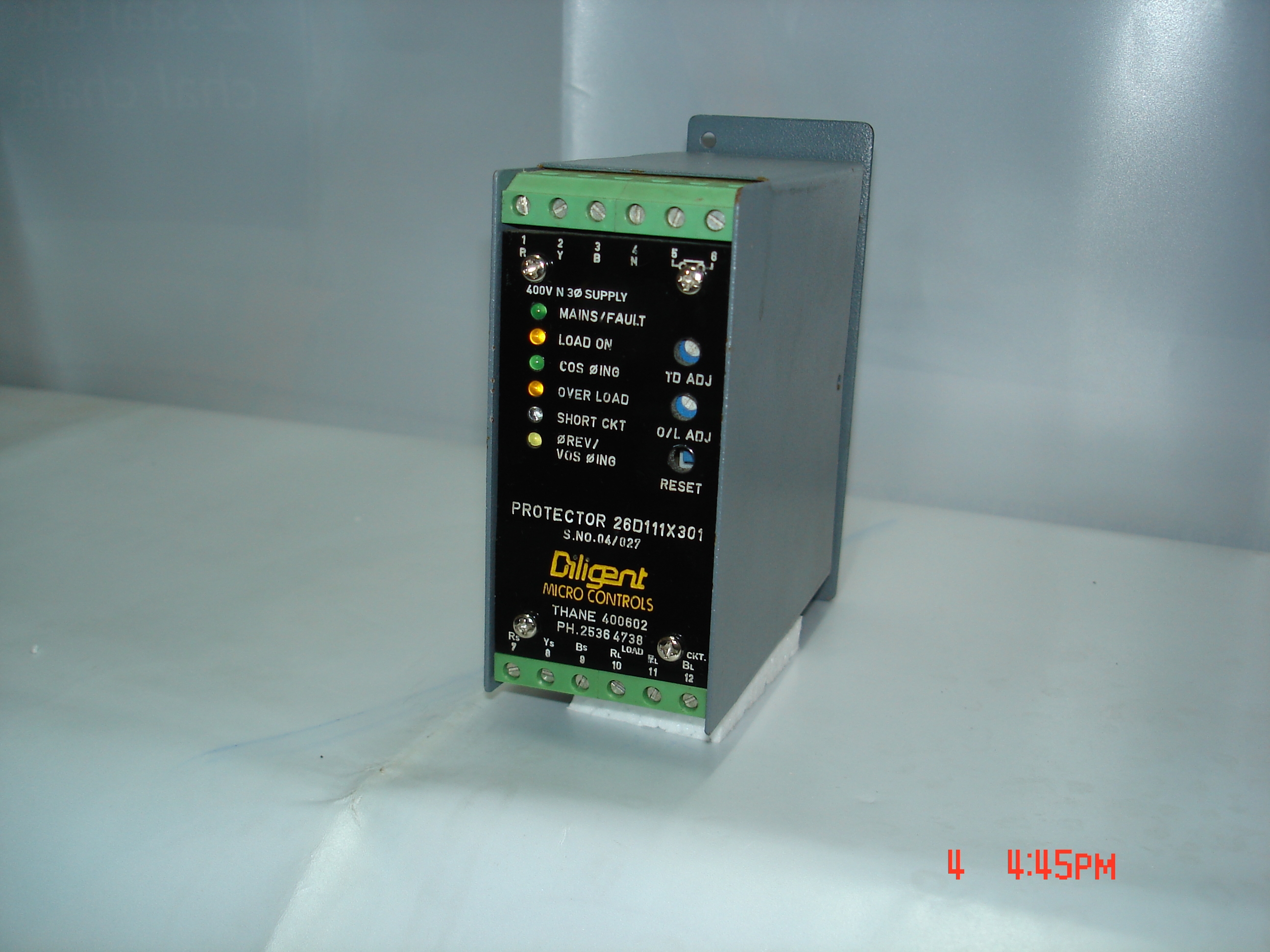
Transient Protector devices are safety devices that are used to protect electrically powered devices from surge currents or transient voltages. These control units are available in various customized sizes and power ratings as per the applications where they are going to be installed.
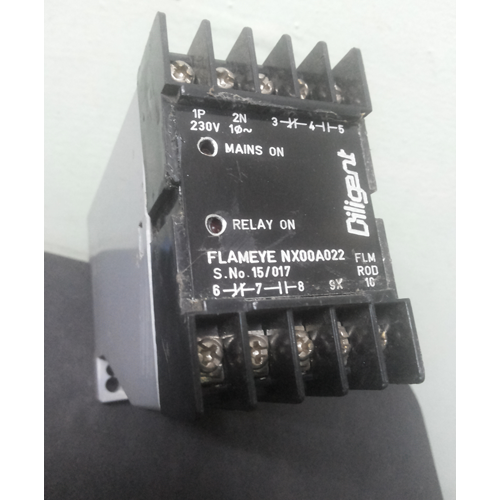
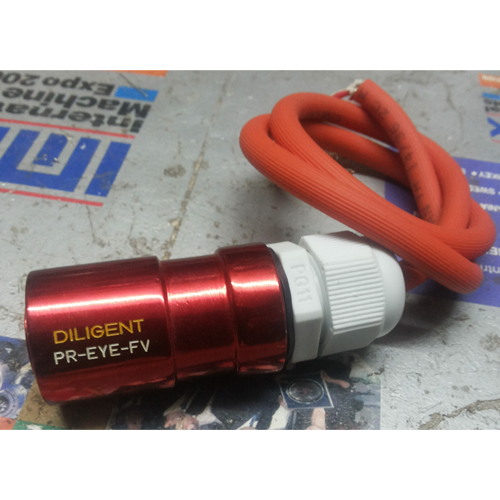
Flame Monitor devices are highly sensitive units that are specially designed for heating and combustion systems to detect the presence of heat. The offered monitoring devices can be delivered to our customers as per orders placed by them at a low price.
Power Modules are reliable integrated circuits that can be used with various electrically powered commercial as well as industrial systems to control input and output power. Customers can get these circuit boards in various sizes and power ratings with an assurance of fast and safe delivery.
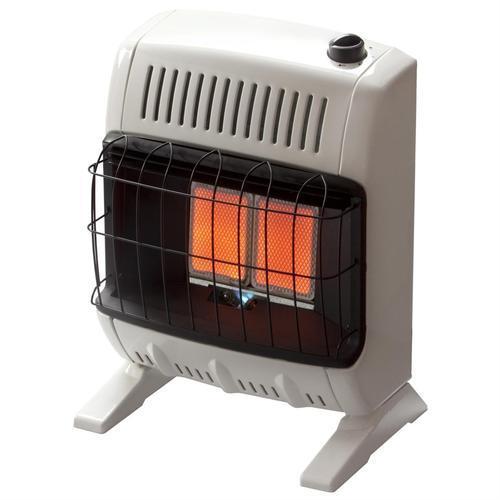
Our company offers many different types of robust and energy-efficient Gas And Tube Heater units that are capable to produce high-temperature heat radiations. These machines are available in different variants as per their size, power ratings, and working principle.
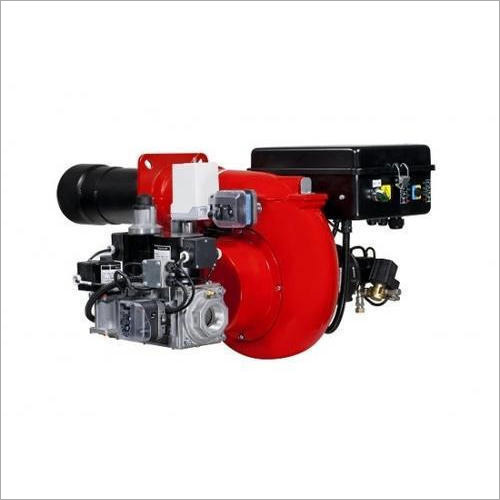
Gas Burner machines are special types of heating systems that are used to generate heat energy using the energy released during gas combustions. These machines are commonly used in power plants, metallurgy, and other industrial sectors.
We are offering best-in-class Electrical Regulator devices that are specially designed for gas-based combustion systems to control the ratio of fuel and air. These control devices are available in various sizes and power ratings as per the applications where they are going to be used.
Flame Sensors are highly sensitive devices that are used to detect the presence of flame and fire. The offered sensor-based devices can be delivered to our clients as per orders placed by them at a reasonable price.
Buy from us AC and DC applications protectors to protect your electrical devices from damage caused by faults and overloads. Not only are these beneficial in safeguarding equipment and devices, but they also ensure personnel safety.
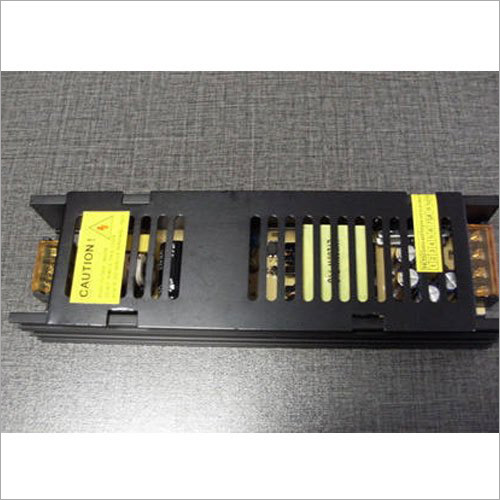
SMPS Board controllers are electronic devices that can be used in commercial and industrial applications to convert AC power into DC. The offered power supply boards come in many different variants as per the clients demand and applications where they are going to be installed.
Buy from our premium range of Power Supply devices that are designed as per electrical engineering standards using best-in-class electrical and electronic components. These units are commonly used within industrial automation and heavy-duty machines to control input power.
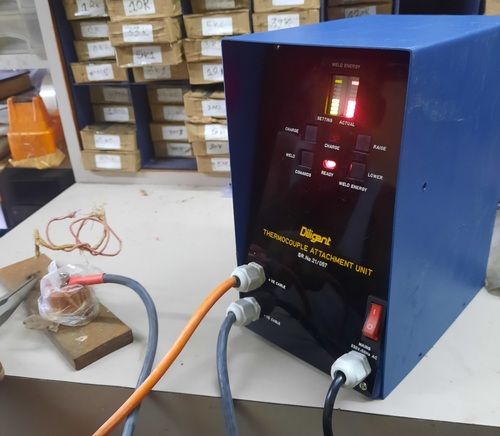
Owing to rich industrial experience and expertise in this business, we are involved in manufacturing of a premium quality Thermocouple Welder. These products are extensively utilized in chemical and electrical industries and widely known for their smooth working. Our products are rigid in construction and highly durable. Our offered products can be availed at market leading prices.
Those seeking compact and specialized electrical devices for their businesses to prevent damage and downtime of electric motors must buy our mini motor protection relay. It is designed to inspect, monitor and safeguard motors from faults, overloads, and abnormal conditions.
We have in stock a protection relay that can be installed for monitoring and protecting single-phase electrical systems as well as equipment from faults and overloads. Businesses utilizing single-phase power must use this device to maintain the reliability of the electrical system.
















 English
English Spanish
Spanish French
French German
German Italian
Italian Chinese (Simplified)
Chinese (Simplified) Japanese
Japanese Korean
Korean Arabic
Arabic Portuguese
Portuguese

